Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Rules to inspect JA4 fingerprints
- 3. Regarding rate-based rules
- 4. Support in WafCharm
- 5. Conclusion
1. Introduction
On March 6, 2025, AWS announced that AWS WAF can now inspect JA4 fingerprints and that JA3 and JA4 fingerprints can also be used as aggregation keys in rate-based rules.
AWS WAF adds JA4 fingerprinting and aggregation on JA3 and JA4 fingerprints for rate-based rules
In this blog post, we are going to take a look at what has been updated.
2. Rules to inspect JA4 fingerprints
The first update lets you create a rule to inspect a JA4 fingerprint. JA4 fingerprint is a value calculated from the information in TLS Client Hello. It is a successor technology to the JA3 fingerprint that can be used to identify a requester. AWS WAF began supporting JA3 fingerprints in September 2023, and JA4 fingerprints have been added with this update.
When you add a rule in AWS WAF and check the Inspect field, you will see that an option called "JA4 fingerprint" has been added. You can only match a value if it is an exact match, so you must check the JA4 fingerprint value you want to match before creating the rule.
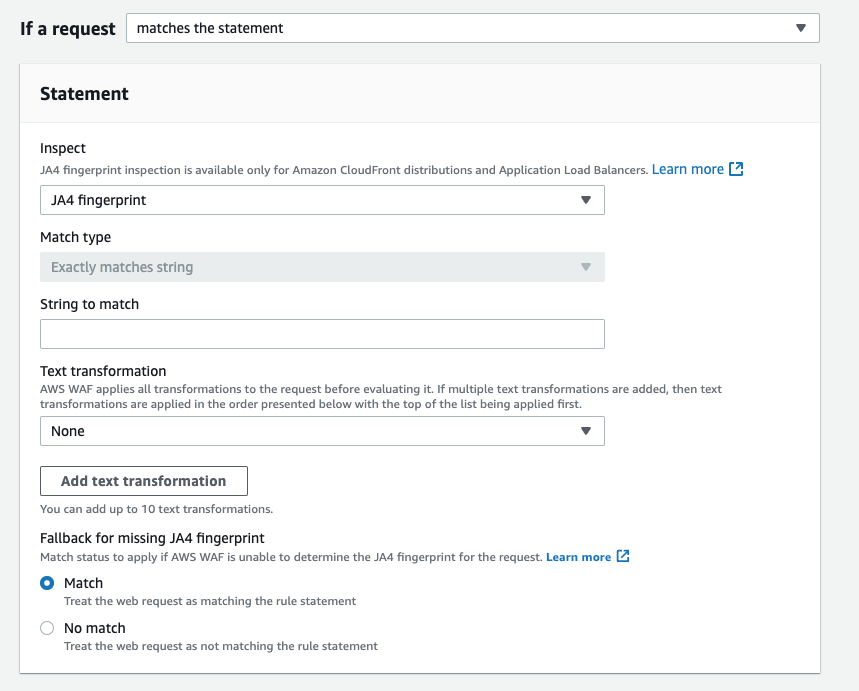
JA4 fingerprint value is available under the ja4Fingerprint field in WAF logs. Check the JA4 fingerprint value of the request you want to block and use that value in the rule. In addition, you must specify a fallback behavior for cases where AWS WAF is unable to calculate the JA4 fingerprint. For more details on the JA4 fingerprint, please refer to the AWS WAF documentation below.
Request components in AWS WAF - JA4 fingerprint
3. Regarding rate-based rules
In rate-based rules, you can specify the JA3 fingerprint and JA4 fingerprint as aggregation keys. For more information about rate-based rules, please refer to the blog posts below.
How to use rate-based rules
You can now specify detailed conditions in rate-based rules
AWS WAF now supports URI paths as custom key in rate-based rules
As stated in the blog posts above, the aggregation key (custom key) is used to aggregate requests based on components other than IP addresses to rate limit requests. If you choose to aggregate requests using the JA3 or JA4 fingerprint, the rate-based rule will be applied when requests with the same JA3 or JA4 fingerprint value exceed the threshold. This option would be useful if you want to identify requesters based on JA3 or JA4 fingerprints.
You can find the "JA3 fingerprint" and "JA4 fingerprint" options in the drop-down menu when selecting the "Rate-based rule" option on the rule configuration page and choosing the "Custom keys" option.
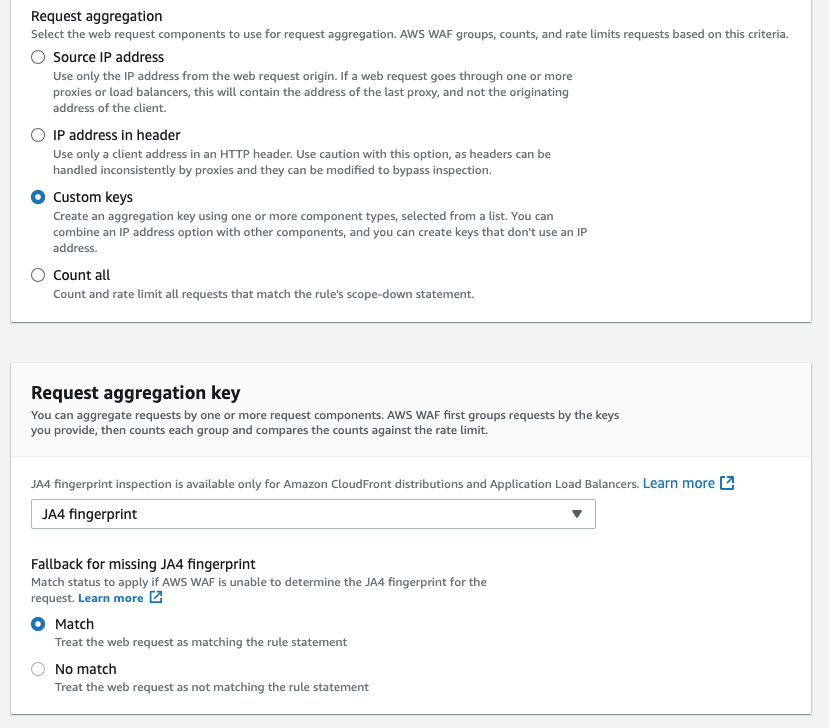
It is similar to aggregating requests using IP addresses, so you don’t need to specify a specific fingerprint value for inspection. However, you must specify a fallback behavior, just like in a regular rule. You can use scope-down statements, which are used to narrow the scope of the requests that the rule tracks, for fingerprints as with other custom keys.
4. Support in WafCharm
As of March 7, 2025, WafCharm has not yet been updated with this change. If you add a regular rule or a rate-based rule using JA4 fingerprints, an error may occur in WafCharm. We apologize for the inconvenience and will update this blog post as soon as we are up to date.
WafCharm has been updated to support this feature. You can now:
- Add a rule using JA3 or JA4 fingerprints from the AWS management console as your own rule.
- Add a rule using JA3 or JA4 fingerprints through WafCharm's customization service.
If you would like to add a rule via the customization service, please contact the WafCharm Support team.
5. Conclusion
With this update, you can now use JA4 fingerprint values in both regular rules and rate-based rules. If you want to block requests from specific bots, you can identify and use their JA4 fingerprint values to block them.
In cases of DDoS attacks where IP addresses change continuously, you might be able to detect the attack using JA4 fingerprint values. While it is difficult to counter DDoS attacks using AWS WAF alone, using JA4 fingerprint values could be one of the useful mitigation strategies.



